Object Storage Disaster Recovery
The Ceph RGW Multi-Site feature is a cross-cluster asynchronous data replication mechanism designed to synchronize object storage data between geographically distributed Ceph clusters, providing High Availability (HA) and Disaster Recovery (DR) capabilities.
TOC
Terminology
Prerequisites
- Prepare two clusters available for deploying Rook-Ceph (Primary and Secondary clusters) with network connectivity between them.
- Both clusters must use the same platform version (v3.12 or later).
- Ensure no Ceph object storage is deployed on either the Primary or Secondary cluster.
- Refer to the Create Storage Service documentation to deploy Operator and create clusters. Do not proceed with object storage pool creation via the wizard after cluster creation. Instead, use CLI tools for configuration as described below.
Architecture
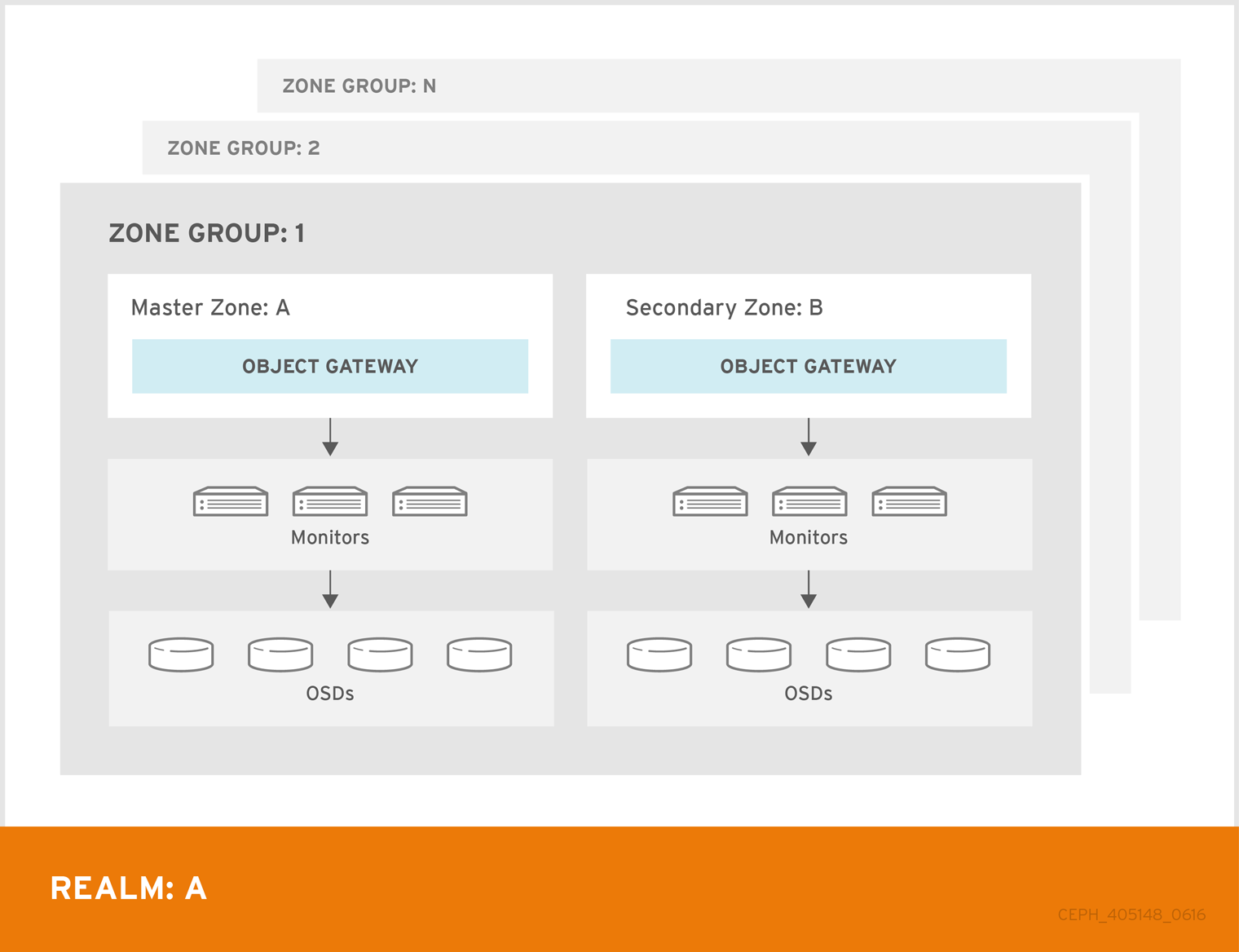
Procedures
This guide provides a synchronization solution between two Zones in the same ZoneGroup.
Create Object Storage in Primary Cluster
This step creates the Realm, ZoneGroup, Primary Zone, and Primary Zone's gateway resources.
Execute the following commands on the Control node of the Primary cluster:
-
Set Parameters
export REALM_NAME=<realm-name>
export ZONE_GROUP_NAME=<zonegroup-name>
export PRIMARY_ZONE_NAME=<primary-zone-name>
export PRIMARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME=<primary-object-store-name>
Parameters description:
<realm-name>: Realm name. <zonegroup-name>: ZoneGroup name. <primary-zone-name>: Primary Zone name. <primary-object-store-name>: Gateway name.
-
Create Object Storage
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
---
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephObjectRealm
metadata:
name: $REALM_NAME
namespace: rook-ceph
---
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephObjectZoneGroup
metadata:
name: $ZONE_GROUP_NAME
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
realm: $REALM_NAME
---
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephObjectZone
metadata:
name: $PRIMARY_ZONE_NAME
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
zoneGroup: $ZONE_GROUP_NAME
metadataPool:
failureDomain: host
replicated:
size: 3
requireSafeReplicaSize: true
dataPool:
failureDomain: host
replicated:
size: 3
requireSafeReplicaSize: true
parameters:
compression_mode: none
preservePoolsOnDelete: false
---
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephBlockPool
metadata:
labels:
cpaas.io/builtin: "true"
name: builtin-rgw-root
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
name: .rgw.root
application: rgw
enableCrushUpdates: true
failureDomain: host
replicated:
size: 3
parameters:
pg_num: "8"
---
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephObjectStore
metadata:
name: $PRIMARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
gateway:
port: 7480
instances: 2
zone:
name: $PRIMARY_ZONE_NAME
EOF
cephobjectrealm.ceph.rook.io/<realm-name> created
cephobjectzonegroup.ceph.rook.io/<zonegroup-name> created
cephobjectzone.ceph.rook.io/<primary-zone-name> created
cephobjectstore.ceph.rook.io/<primary-object-store-name> created
-
Obtain the UID of the ObjectStore
export PRIMARY_OBJECT_STORE_UID=$(kubectl -n rook-ceph get cephobjectstore $PRIMARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME -o jsonpath='{.metadata.uid}')
-
Create an external access Service
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: rook-ceph-rgw-$PRIMARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME-external
namespace: rook-ceph
labels:
app: rook-ceph-rgw
rook_cluster: rook-ceph
rook_object_store: $PRIMARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME
ownerReferences:
- apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephObjectStore
name: $PRIMARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME
uid: $PRIMARY_OBJECT_STORE_UID
spec:
ports:
- name: rgw
port: 7480
targetPort: 7480
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: rook-ceph-rgw
rook_cluster: rook-ceph
rook_object_store: $PRIMARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
EOF
-
Add external endpoints to the CephObjectZone.
IP=$(kubectl get nodes -l 'node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane' -o jsonpath='{.items[0].status.addresses[?(@.type=="InternalIP")].address}' | cut -d ' ' -f1 | tr -d '\n')
PORT=$(kubectl -n rook-ceph get svc rook-ceph-rgw-$PRIMARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME-external -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}')
ENDPOINT=http://$IP:$PORT
kubectl -n rook-ceph patch cephobjectzone $PRIMARY_ZONE_NAME --type merge -p "{\"spec\":{\"customEndpoints\":[\"$ENDPOINT\"]}}"
Obtain access-key and secret-key
kubectl -n rook-ceph get secrets $REALM_NAME-keys -o jsonpath='{.data.access-key}'
kubectl -n rook-ceph get secrets $REALM_NAME-keys -o jsonpath='{.data.secret-key}'
This section explains how to create the Secondary Zone and configure synchronization by pulling Realm information from the Primary cluster.
Execute the following commands on the Control node of the Secondary cluster:
-
Set Parameters
export REALM_NAME=<realm-name>
export ZONE_GROUP_NAME=<zonegroup-name>
export REALM_ENDPOINT=<realm-endpoint>
export ACCESS_KEY=<access-key>
export SECRET_KEY=<secret-key>
export SECONDARY_ZONE_NAME=<secondary-zone-name>
export SECONDARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME=<secondary-object-store-name>
Parameters description:
<realm-name>: Realm name.<zone-group-name>: ZoneGroup name.<realm-endpoint>: External address obtained from the Primary cluster.<access-key>: AK obtain from here.<secret-key>: SK obtain from here.<secondary-zone-name>: Secondary Zone name.<secondary-object-store-name>: Secondary Gateway name.
-
Create Secondary Zone and Configure Realm Sync
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: $REALM_NAME-keys
namespace: rook-ceph
data:
access-key: $ACCESS_KEY
secret-key: $SECRET_KEY
---
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephObjectRealm
metadata:
name: $REALM_NAME
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
pull:
endpoint: $REALM_ENDPOINT
---
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephObjectZoneGroup
metadata:
name: $ZONE_GROUP_NAME
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
realm: $REALM_NAME
---
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephObjectZone
metadata:
name: $SECONDARY_ZONE_NAME
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
zoneGroup: $ZONE_GROUP_NAME
metadataPool:
failureDomain: host
replicated:
size: 3
requireSafeReplicaSize: true
dataPool:
failureDomain: host
replicated:
size: 3
requireSafeReplicaSize: true
preservePoolsOnDelete: false
---
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephBlockPool
metadata:
labels:
cpaas.io/builtin: "true"
name: builtin-rgw-root
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
name: .rgw.root
application: rgw
enableCrushUpdates: true
failureDomain: host
replicated:
size: 3
parameters:
pg_num: "8"
---
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephObjectStore
metadata:
name: $SECONDARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
gateway:
port: 7480
instances: 2
zone:
name: $SECONDARY_ZONE_NAME
EOF
-
Obtain UID of Secondary Gateway
export SECONDARY_OBJECT_STORE_UID=$(kubectl -n rook-ceph get cephobjectstore $SECONDARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME -o jsonpath='{.metadata.uid}')
-
Create an external access Service
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: rook-ceph-rgw-$SECONDARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME-external
namespace: rook-ceph
labels:
app: rook-ceph-rgw
rook_cluster: rook-ceph
rook_object_store: $SECONDARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME
ownerReferences:
- apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephObjectStore
name: $SECONDARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME
uid: $SECONDARY_OBJECT_STORE_UID
spec:
ports:
- name: rgw
port: 7480
targetPort: 7480
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: rook-ceph-rgw
rook_cluster: rook-ceph
rook_object_store: $SECONDARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
EOF
-
Add external endpoints to the Secondary CephObjectZone
IP=$(kubectl get nodes -l 'node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane' -o jsonpath='{.items[0].status.addresses[?(@.type=="InternalIP")].address}' | cut -d ' ' -f1 | tr -d '\n')
PORT=$(kubectl -n rook-ceph get svc rook-ceph-rgw-$SECONDARY_OBJECT_STORE_NAME-external -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}')
ENDPOINT=http://$IP:$PORT
kubectl -n rook-ceph patch cephobjectzone $SECONDARY_ZONE_NAME --type merge -p "{\"spec\":{\"customEndpoints\":[\"$ENDPOINT\"]}}"
Check Ceph Object Storage Synchronization Status
Execute the following commands in the rook-ceph-tools pod of the Secondary cluster
# enter rook-ceph-tools pod
kubectl -n rook-ceph exec -it $(kubectl -n rook-ceph get po -l app=rook-ceph-tools -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{@.metadata.name}') -- bash
radosgw-admin sync status
Output example
realm 962d6b80-b218-4fc8-8198-e498fabc4e9d (relam-primary)
zonegroup 9de3acd7-0b01-4a04-ac84-1421c6103a16 (zonegroup-primary)
zone 7b3ce7f5-7090-46f6-afb1-d1bb156053da (zone-secondary)
current time 2025-12-04T06:27:15Z
zonegroup features enabled: resharding
disabled: compress-encrypted
metadata sync syncing
full sync: 0/64 shards
incremental sync: 64/64 shards
metadata is caught up with master
data sync source: 6319ca70-964e-47be-8b96-7c5bf5a128b1 (zone-primary)
syncing
full sync: 0/128 shards
incremental sync: 128/128 shards
data is caught up with source
metadata is caught up with master and data is caught up with source means sync status is healthy.
Failover
When the Primary cluster fails, it is necessary to promote the Secondary Zone to the Primary Zone. After the switch, the Secondary Zone's gateway can continue to provide object storage services.
Procedures
Execute the following commands in the rook-ceph-tools pod of the Secondary cluster
# enter rook-ceph-tools pod
kubectl -n rook-ceph exec -it $(kubectl -n rook-ceph get po -l app=rook-ceph-tools -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{@.metadata.name}') -- bash
# Make the recovered zone the master and default zone
radosgw-admin zone modify --rgw-realm=<realm-name> --rgw-zonegroup=<zone-group-name> --rgw-zone=<secondary-zone-name> --master
# Update the period so that the changes take effect
radosgw-admin period update --commit --rgw-realm=<realm-name> --rgw-zonegroup=<zone-group-name>
Parameters
<realm-name>: Realm name.<zone-group-name>: Secondary Zone Group name.<secondary-zone-name>: Secondary Zone name.
Failback
Once the failed cluster is recovered on the primary site and you want to failback from secondary site, follow the below stepss
Procedures
Execute the following commands in the rook-ceph-tools pod of the Primary cluster
# enter rook-ceph-tools pod
kubectl -n rook-ceph exec -it $(kubectl -n rook-ceph get po -l app=rook-ceph-tools -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{@.metadata.name}') -- bash
# check sync status, wait for sync from secondary site
radosgw-admin sync status
# realm 962d6b80-b218-4fc8-8198-e498fabc4e9d (relam-primary)
# zonegroup 9de3acd7-0b01-4a04-ac84-1421c6103a16 (zonegroup-primary)
# zone 6319ca70-964e-47be-8b96-7c5bf5a128b1 (zone-primary)
# current time 2025-12-04T07:18:26Z
# zonegroup features enabled: resharding
# disabled: compress-encrypted
# metadata sync syncing
# full sync: 0/64 shards
# incremental sync: 64/64 shards
# metadata is caught up with master
# data sync source: 7b3ce7f5-7090-46f6-afb1-d1bb156053da (zone-secondary)
# syncing
# full sync: 0/128 shards
# incremental sync: 128/128 shards
# data is caught up with source
# Make the recovered zone the master and default zone
radosgw-admin zone modify --rgw-realm=<realm-name> --rgw-zonegroup=<zone-group-name> --rgw-zone=<primary-zone-name> --master
# Update the period so that the changes take effect
radosgw-admin period update --commit --rgw-realm=<realm-name> --rgw-zonegroup=<zone-group-name>
Parameters
<realm-name>: Realm name.<zone-group-name>: Zone Group name.<primary-zone-name>: Primary Zone name.
